Effect of intermittent fasting on behavioral, biochemical and histopathological parameters in rats under Acrylamide exposure
Abstract
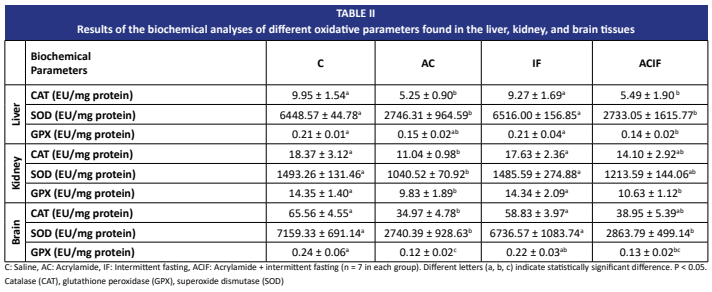
Acrylamide is a known neurotoxic and potentially carcinogenic compound. It remains as a major public health concern due to its widespread presence in heat-processed foods. Despite extensive research on acrylamide-induced toxicity, effective dietary strategies to mitigate its harmful impact remain limited. Intermittent fasting has recently emerged as a promising metabolic intervention shown to enhance cellular stress resistance and improve antioxidant capacity. This study was designed to investigate the effects of intermittent fasting on acrylamide-induced toxicity in rats. Wistar rats were randomly divided into four groups: control, acrylamide, intermittent fasting, and acrylamide + intermittent fasting. Intermittent fasting was applied every other day, while acrylamide was administered intraperitoneally at a dose of 30 mg/kg/day, three times per week. On day 28, behavioral assessments were performed using the Elevated Plus Maze, Open Field Test, hotplate, and rotarod tests. Biochemical analyses were conducted on blood samples, and oxidative stress parameters Catalase, Glutathione peroxidase, Superoxide dismutase were measured in liver, kidney, and brain tissues. Histopathological evaluations were also carried out. Histopathological findings indicated tissue damage in the acrylamide group and partial improvement in the acrylamide + intermittent fasting group. In the rotarod test, performance of the acrylamide + intermittent fasting group was similar to the control group, suggesting a protective effect. Catalase, Glutathione peroxidase, and Superoxide dismutase levels showed partial amelioration in kidney and brain tissues due to intermittent fasting. The results suggest that intermittent fasting may exert a protective effect against acrylamide-induced oxidative stress and behavioral impairments in rats. These findings highlight the potential of intermittent fasting as a non-pharmacological strategy to mitigate acrylamide toxicity.
Downloads
References
Arıhan O, Seringeç NB, Gürel EI, Dikmenoğlu NH. Effects of oral acrylamide intake on blood viscosity parameters in rats. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. [Internet]. 2011; 47(1):45-52. doi: https://doi.org/qkrp DOI: https://doi.org/10.3233/CH-2010-1364
Belai A, Burnstock G. Acrylamide-induced neuropathic changes in rat enteric nerves: similarities with effects of streptozotocin-diabetes. Auton Neurosci. [Internet]. 1996; 58(1-2):56-62. doi: https://doi.org/bjsf3n DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1838(95)00117-4
Pelucchi C, Galeone C, Levi F, Negri E, Franceschi S, Talamini R, Bosetti C, Giacosa A, La Vecchia C. Dietary acrylamide and human cancer. Int. J. Cancer. [Internet]. 2006; 118(2):467-471. doi: https://doi.org/fd3dtv DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.21336
Riboldi BP, Vinhas ÁM, Moreira JD. Risks of dietary acrylamide exposure: A systematic review. Food Chem. [Internet]. 2014; 157:310-322. doi: https://doi.org/gp4pmk DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.02.046
Nowosad K, Sujka M. Effect of various types of intermittent fasting (IF) on weight loss and improvement of diabetic parameters in human. Curr. Nutr. Rep. [Internet]. 2021; 10:146-154. doi: https://doi.org/gpstdt DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13668-021-00353-5
Varady KA, Cienfuegos S, Ezpeleta M, Gabel K. Cardiometabolic benefits of intermittent fasting. Annu. Rev. Nutr. [Internet]. 2021; 41:333-361. doi: https://doi.org/gnzk9f DOI: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-052020-041327
Vitale R, Kim Y. The effects of intermittent fasting on glycemic control and body composition in adults with obesity and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. [Internet]. 2020; 18(10):450-461. doi: https://doi.org/gsvnk5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/met.2020.0048
Vasim I, Majeed CN, DeBoer MD. Intermittent fasting and metabolic health. Nutrients. [Internet]. 2022; 14(3):631. doi: https://doi.org/g9wmv7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14030631
Francis N. Intermittent fasting and brain health: Efficacy and potential mechanisms of action. OBM Geriatrics. [Internet]. 2020; 4(2):121. doi: https://doi.org/qkrq
Gudden J, Arias-Vasquez A, Bloemendaal M. The effects of intermittent fasting on brain and cognitive function. Nutrients. [Internet]. 2021; 13(9):3166. doi: https://doi.org/gpk4qr DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13093166
Neth BJ, Bauer BA, Benarroch EE, Savica R. The role of intermittent fasting in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurol. [Internet]. 2021; 12:682184. doi: https://doi.org/gkbfxx DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.682184
Clifton KK, Ma CX, Fontana L, Peterson LL. Intermittent fasting in the prevention and treatment of cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. [Internet]. 2021; 71(6):527-546. doi: https://doi.org/gpwf6s DOI: https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21694
Berthelot E, Etchecopar-Etchart D, Thellier D, Lancon C, Boyer L, Fond G. Fasting interventions for stress, anxiety and depressive symptoms: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. [Internet]. 2021; 13(11):3947. doi: https://doi.org/qkrr DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113947
Fernandez-Rodriguez R, Martinez-Vizcaino V, Mesas AE, Notario-Pacheco B, Medrano M, Heilbronn LK. Does intermittent fasting impact mental disorders? A systematic review with meta-analysis. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. [Internet]. 2023; 63(32):11169-11184. doi: https://doi.org/qkrs DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2022.2088687
Tikoo K, Tripathi DN, Kabra DG, Sharma V, Gaikwad AB. Intermittent fasting prevents the progression of type I diabetic nephropathy in rats and changes the expression of Sir2 and p53. FEBS Lett. [Internet]. 2007; 581(5):1071- 1078. doi: https://doi.org/fb65m3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2007.02.006
Xia E, Rao G, Van Remmen H, Heydari AR, Richardson A. Activities of antioxidant enzymes in various tissues of male Fischer 344 rats are altered by food restriction. J. Nutr. [Internet]. 1995; 125(2):195-201. doi: https://doi.org/pp6g DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/125.2.195
Aebi H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. [Internet] 1984;105:121-126. https://doi.org/dnf7v9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Paglia DE, Valentine WN. Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J. Lab. Clin. Med. [Internet]. 1967 [cited 10 Nov 2025]; 70(1):158-169. Available in: https://goo.su/FGBDzm
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y. A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin. Chem. [Internet]. 1988; 34(3):497-500. doi: https://doi.org/gj74fn DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/34.3.497
Abdel-Wahhab M, Nada S, Arbid M. Ochratoxicosis: prevention of developmental toxicity by L-methionine in rats. J. Appl. Toxicol. 1999; 19(1):7-12. doi: https://doi.org/drjc5b DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1263(199901/02)19:1<7::AID-JAT529>3.0.CO;2-G
Şener G, Ekşioğlu-Demiralp E, Cetiner M, Ercan F, Şirvancı S, Gedik N, Yeğen BC. L-Carnitine ameliorates methotrexate-induced oxidative organ injury and inhibits leukocyte death. Cell. Biol. Toxicol. [Internet]. 2006; 22:47-60. doi: https://doi.org/cnsczn DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-006-0025-0
Gür F, Cengiz M, Gür B, Cengiz O, Sarıçiçek O, Ayhancı A. Therapeutic role of boron on acrylamide-induced nephrotoxicity, cardiotoxicity, neurotoxicity, and testicular toxicity in rats: Effects on Nrf2/Keap-1 signaling pathway and oxidative stress. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. [Internet]. 2023; 80:127274. doi: https://doi.org/qkrv DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2023.127274
Quan W, Li M, Jiao Y, Zeng M, He Z, Shen Q, Chen J. Effect of Dietary Exposure to Acrylamide on Diabetes- Associated Cognitive Dysfunction from the Perspectives of Oxidative Damage, Neuroinflammation, and Metabolic Disorders. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022; 70(14):4445-4456. doi: https://doi.org/qkrw DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.2c00662
Kopańska M, Łagowska A, Kuduk B, Banaś-Ząbczyk A. Acrylamide Neurotoxicity as a Possible Factor Responsible for Inflammation in the Cholinergic Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022; 23(4):2030. doi: https://doi.org/gp49sc DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23042030
Elias A, Padinjakara N, Lautenschlager NT. Effects of intermittent fasting on cognitive health and Alzheimer’s disease. Nutr. Rev. [Internet]. 2023; 81(9):1225-1233. doi: https://doi.org/qkrx DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuad021
Yang Q, Li M, Liu J, Zhang L, Yuan R, Xu Y, Zheng J, Cao S, Dai H, Liao M, Lv M, Chen X, Guo Y, Xie X, Zhang L, Chen X, Liang W. Intermittent fasting ameliorates neuronal ferroptosis and cognitive impairment in mice after traumatic brain injury. Nutrition. [Internet]. 2023; 109:111992. doi: https://doi.org/qkrz DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2023.111992
Chen W, Wang L, Zhou A, Fan C, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Rong S, Wang T. The benefits of intermittent fasting: A review of possible mechanisms on central neurological disorders. Acta Aliment. [Internet]. 2023; 52(1):1-11. doi: https://doi.org/qkr2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1556/066.2022.00230
Elesawy BH, Raafat BM, Muqbali AA, Abbas AM, Sakr HF. The Impact of Intermittent Fasting on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, Neurotrophin 3, and Rat Behavior in a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Brain Sci. 2021; 11(2):242. doi: https://doi.org/qkr3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11020242
Ebrahim HA, El-Gamal R, Sherif RN. Intermittent Fasting Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Cerebellar Changes in Rats: Involvement of TNF-α, Autophagy, and Oxidative Stress. Cells Tissues Organs. 2021; 210(5-6):351-367. doi: https://doi.org/qkr4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1159/000519088
Ye Y, Chai SF, Li XR, Wu MN, Cai HY, Wang ZJ. Intermittent fasting and Alzheimer’s disease—Targeting ketone bodies as a potential strategy for brain energy rescue. Metab. Brain Dis. 2023; 39(1):129-146. https://doi.org/qkr5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01288-2
Kaplan ML, Murphy SD. Effect of acrylamide on rotarod performance and sciatic nerve β-glucuronidase activity of rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. [Internet]. 1972; 22(2):259-268. doi: https://doi.org/ddtrph DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0041-008X(72)90176-7
Tanii H, Hashimoto K. Neurotoxicity of acrylamide and related compounds in rats. Effects on rotarod performance, morphology of nerves and neurotubulin. Arch. Toxicol. [Internet]. 1983; 54(3):203-213. doi: https://doi.org/dpb7wg DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01239204
Huang Z, Wang S, Yang Y, Lou J, Liu Z, Liu Z, Yong H, Shan S, Song F. Mitochondrial dysfunction promotes the necroptosis of Purkinje cells in the cerebellum of acrylamide-exposed rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023; 171:113522. doi: https://doi.org/qksd DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2022.113522
Pak M, Bozkurt S, Pınarbaşı A, Öz Arslan D, Aksungar FB. Effects of Prolonged Intermittent Fasting Model on Energy Metabolism and Mitochondrial Functions in Neurons. Ann. Neurosci. 2022; 29(1):21-31. doi: https://doi.org/qksf DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/09727531211072303
Brocchi A, Rebelos E, Dardano A, Mantuano M, Daniele G. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Brain Metabolism. Nutrients. [Internet]. 2022; 14(6):1275. doi: https://doi.org/qksg DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14061275
Ling B, Authier N, Balayssac D, Eschalier A, Coudore F. Assessment of nociception in acrylamide-induced neuropathy in rats. Pain. [Internet]. 2005; 119(1-3):104-112. doi: https://doi.org/dvbzsv DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2005.09.021
Vanitha S, Thiagarajan VRK, Muthuraman A, Krishnan S, Aruna A, Tharabai R. Pharmacological evaluation of methanolic leaf extract of Swietenia mahagoni on acrylamide-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Toxicol. Ind. Health. [Internet]. 2015; 31(12):1185-1194. doi: https://doi.org/f3px9p DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233713491808
Ajibare A, Akintoye O, Oriowo O, Asuku A, Adeola I, Ayoola A. Zinc Ameliorates Acrylamide-Induced Cognitive Impairment in Male Wistar Rats: Modulation of Oxidative Stress, Neuro-inflammation, and Neurotrophic Pathways. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. [Internet]. 2024; 203:4273-4282. doi: https://doi.org/qksh DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-024-04490-0
Cerrah S, Ozcicek F, Gundogdu B, Cicek B, Coban TA, Suleyman B, Altuner D, Bulut S, Suleyman H. Carvacrol prevents acrylamide-induced oxidative and inflammatory liver damage and dysfunction in rats. Front. Pharmacol. [Internet]. 2023; 14:1161448. doi: https://doi.org/qksj DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2023.1161448
Ibaokurgil F, Aydin H, Yildirim S, Sengul E. Melatonin alleviates oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and DNA damage in acrylamide–induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. [Internet]. 2023; 13(3):121-130. doi: https://doi.org/qksk DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/2221-1691.372285
Guo H, Bechtel-Walz W. The Interplay of Autophagy and Oxidative Stress in the Kidney: What Do We Know? Nephron. [Internet]. 2023; 147(10):627-642. doi: https://doi.org/qksm DOI: https://doi.org/10.1159/000531290
Abdel-Rahman M, Hussein AA, Ahmed-Farid OA, Sawi AA, Abdel-Moneim AE. Intermittent fasting alerts neurotransmitters and oxidant/antioxidant status in the brain of rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 2024; 39(7):1291-1305. doi: https://doi.org/qksn DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-024-01415-7
Agbonifo-Chijiokwu E, Nwangwa KE, Oyovwi MO, Ben- Azu B, Naiho AO, Emojevwe V, Ohwin EP, Ehiwarior AP, Ojugbeli ET, Nwabuoku SU, Moke EG, Oghenetega BO. Underlying biochemical effects of intermittent fasting, exercise and honey on streptozotocin-induced liver damage in rats. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. [Internet]. 2023; 22(1):515-527. doi: https://doi.org/qksp DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-022-01173-2
Sharsher SI, Ahmed AI, Metwally M, Arisha AH, Ahmed KE. Intermittent Fasting Decreases Oxidative Stress Parameters and Increases Total Antioxidant Capacity. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022; 12(5):6763–6775. doi: https://doi.org/qksq DOI: https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC125.67636775
Ceylani T, Tekeli HT, Eranıl I, Yılmaz Ertük F, Keskin S. Intermittent Fasting Modulates Age-Dependent Morphological and Histological Hepatic Changes on Liver Tissue in Wistar Rats. In: Oral O, Nalci KA, editor. New Frontıers In Health Scıences. Türkiye: Duvar Yayınları; 2023; 8:125-142. Available in: https://goo.su/16Y6Gq
Al-Kazimi N, Jarrar Y, Abdul-Wahab G, Alsayed AR, Madani A, Abulebdah D, Musleh RS, jarrar Q, Al-Ameer HJ, Al- Awaida W, Abdullah E. Effects of intermittent fasting on the histology and mRNA expression of major drug- metabolizing cyp450s in the liver of diabetic mice. Libyan J. Med. [Internet]. 2023; 18(1):2270188. doi: https://doi.org/qkss DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/19932820.2023.2270188
Priyono D, Harun H, Viotra D, Dasril ZM. Effect of Ramadan Fasting on DNA Repair, Immune System, Inflammation and Cognitive Function in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: A Systematic Literature Review. Bio. Sci. Med. J. Biomed. Transl. Res. [Internet]. 2023; 7(4):3252- 3256. doi: https://doi.org/qkst DOI: https://doi.org/10.37275/bsm.v7i4.809
Hafez SMNA, Elbassuoni E. Dysfunction of aged liver of male albino rats and the effect of intermitted fasting; Biochemical, histological, and immunohistochemical study. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022; 103:108465. doi: https://doi.org/qksv DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108465
Jang Y, Kim YS, Kim SR, Lee DW, Lee SB, Kim IY. Intermittent Fasting Protects Against the Progression from Acute Kidney Injury to Chronic Kidney Disease. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(1):119. doi: https://doi.org/g89gtf DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14010119
Rifaai RA, El-Tahawy NFG, Abozaid SMM, Abdelwahab Intermittent Fasting Ameliorates Age-Induced Morphological Changes in Aged Albino Rat Kidney via Autophagy Activation and Reduction of Apoptosis and Inflammation. Microsc. Microanal. 2025; 31(1):ozae102. doi: https://doi.org/qksw DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/mam/ozae102